Authors: Lur Epelde, Anders Lanzén, Iker Martín, Susana Virgel, Iker Mijangos, Gerardo Besga, Carlos Garbisu
Journal: Chemosphere
Vol: 220, 600-610
Date: 2019
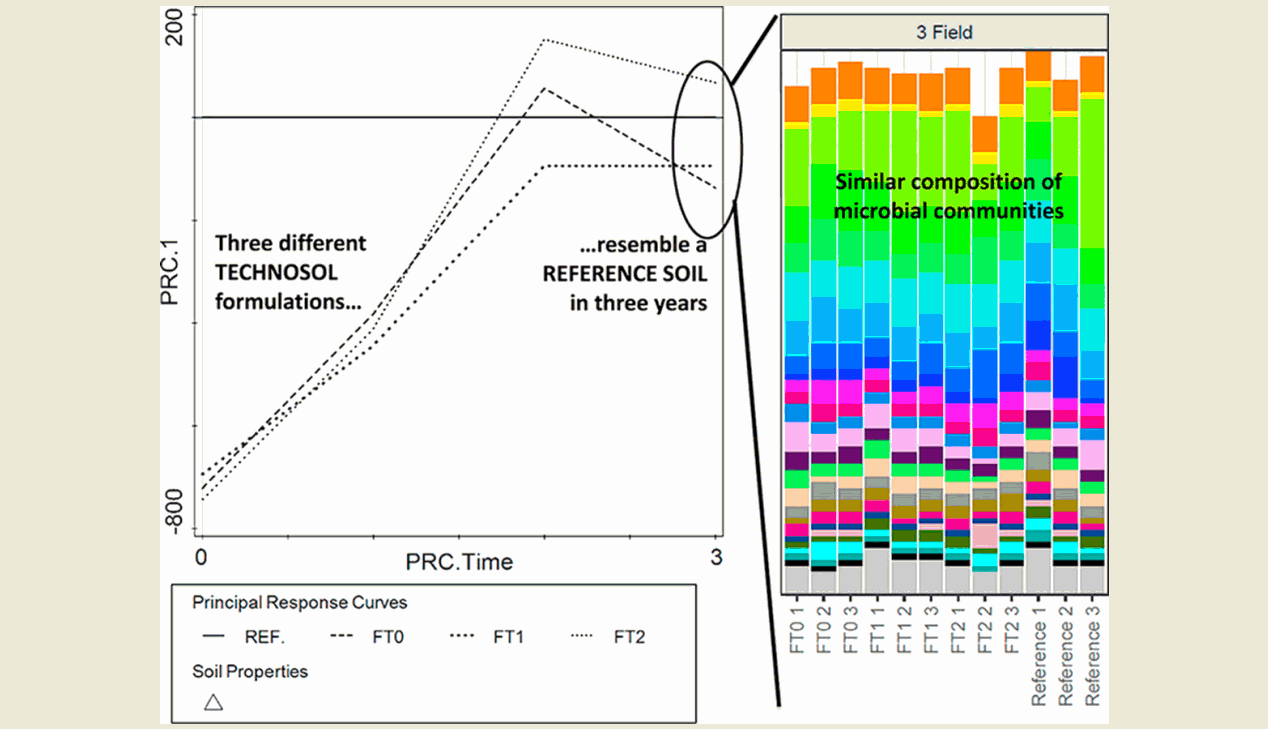
Technosols can be used to rehabilitate degraded land and reuse wastes. Ideally, these newly formed soils should also fulfil the main soil functions. In this study, initially, we characterized the physicochemical and microbial properties of different formulations and their ingredients (i.e., dirt from a waste recovery plant, recycled bentonite, sewage sludge). When these technosols were then used for the rehabilitation of a quarry, the evolution of such properties was monitored for three consecutive years. Physicochemical and microbial properties were compared to those of a reference soil from a nearby forest. Diversity and composition of prokaryotes and eukaryotes were determined using 16S and 18S rRNA amplicon sequencing. Three years after establishment, as much as 78.8% and 63.9% of the prokaryotic and eukaryotic orders, respectively, were shared between the technosols and the reference forest soil. Although technosols initially showed lower values of CO2 emission, compaction and functional diversity (Biolog EcoPlates™), at the end of the study these values were similar to those observed in the reference forest soil. It was concluded that the microbiota of the studied technosols resembles that of the nearby forest soil after just three years of establishment.