Authors: Lur Epelde, Maddalen Mendizabal, Laura Gutiérrez, Ainara Artetxe, Carlos Garbisu, Efrén Feliu
Journal: Urban Forestry & Urban Greening
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ufug.2021.127433
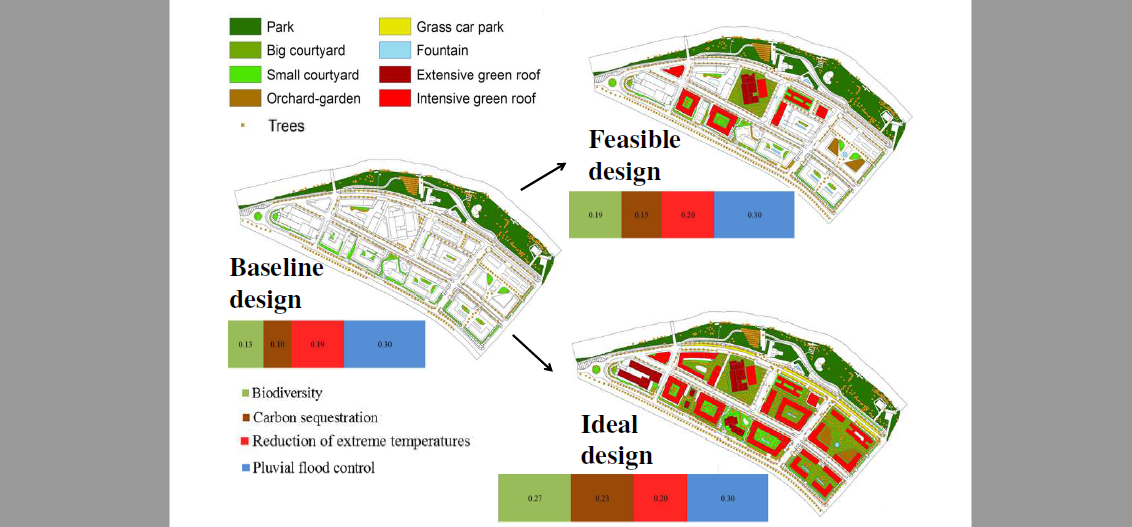
Nature-based solutions (NBSs) enhance the potential for mitigation and adaptation to climate change in cities. Among the environmental benefits offered by these measures, enhanced biodiversity, increased carbon storage, reduction of extreme temperatures, and pluvial flood control are crucial. The purpose of this study was to establish an integrated methodology for quantifying the benefits of NBSs and complementary measures and to apply it in a neighbourhood of Donostia-San Sebastián (Spain), where two alternative designs that incorporated NBSs and complementary measures were designed. Then, the individual effectiveness of the four variables was measured using both in-situ measurements and modelling approaches. For the integrated effectiveness, a multi-criteria decision analysis was employed. Both the ‘feasible’ design and the ‘ideal’ one led to an increase in biodiversity (46 and 108%, respectively) and carbon storage (50 and 130%, respectively). When considering each measure independently, putting soil provided the highest benefits for carbon capture and biodiversity; meanwhile, planting woody species and installing light-coloured permeable pavements and water fountains reduced the mean radiant temperature by 26.5 K and the air temperature by 0.5 and 2.5 K, respectively, in specific places. Finally, the importance of quantifying the multiple environmental benefits of NBSs for the selection of climate-smart options in urban planning has been highlighted.